The first time I heard the word “Blockchain” was 3 years ago at a family gathering. The word created a lot of buzz amongst my very entrepreneurial family, and every working adult over the age of 35 had something to contribute to the discussion. Naturally, I was curious and I listened in on the whole conversation. The initial conclusion I came to was that,
- The whole concept seemed super sketchy.
- Blockchain and Bitcoin are the same. (They’re quite different and I’ll get into it later.)
After poring through articles and probably a few days’ worth of research, I gained enough knowledge about the topic to hopefully succeed at my attempt to demystify it for those of you who don’t know enough about it yet.
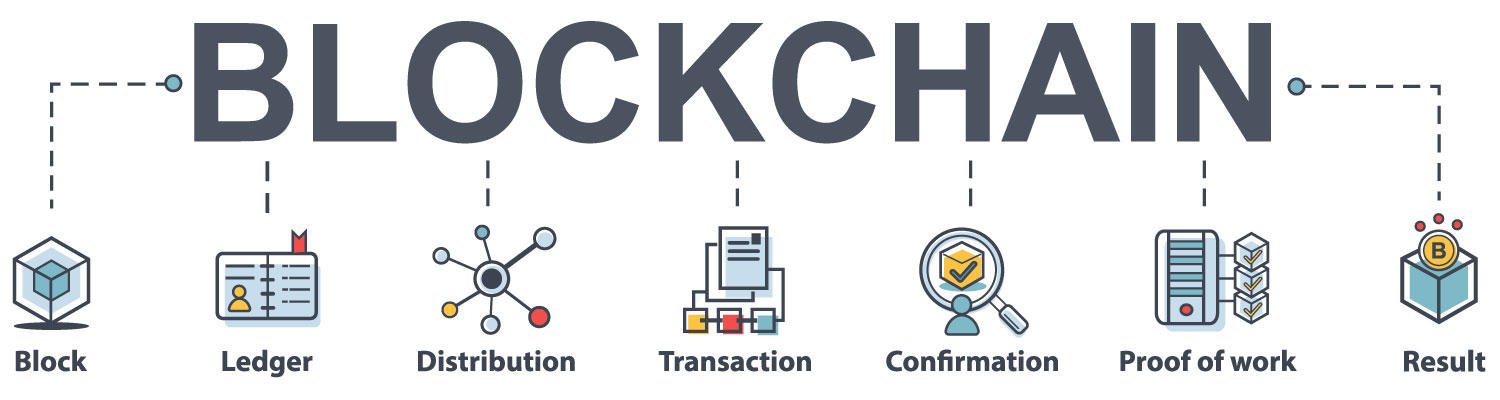
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain technology enables cryptocurrencies to function in the same way that the internet enables email. A Blockchain's operation works on Blockchain technology
“Cryptocurrencies are digital currencies in which transactions are verified and records maintained by a decentralized system using cryptography, rather than by a centralized authority.”
Imagine that banks don't exist. Each person is their bank. You don't have to pay any sort of bank fees and all your money is stored in an online wallet of your own. You do not have to take a bank’s permission or authorization to move your money. This is basically what Blockchain is. Blockchain is an online ledger where the transactions cannot be altered and the records are stored in multiple places on a computer network, hence it is also distributed. These two features are key in understanding why Blockchain is important; the fact that it is distributed and cannot be changed concludes that it is always trustworthy and are not privy to attacks, thus being as safe as possible.
Every tiny bit of information is stored on something called a ‘block’ and each block is dependent on the information stored in the previous block. This forms a chain of information or transactions and this is why the name “Blockchain” was coined.
Blockchain was first implemented by Satoshi Nakamoto (No one knows who this is) when they created and deployed Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency (and this is how they differ; Blockchain: technology and Bitcoin: cryptocurrency based on Blockchain technology.)

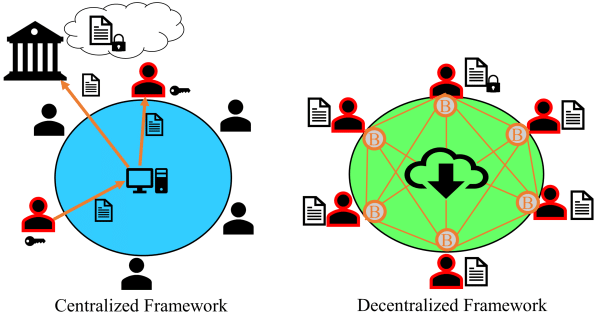
Centralization vs. Decentralization
Centralization is the general norm of how everything works these days. It involves an administrator that has authority over all the data and functions of the said platform. For example, when you use Instagram, the team that runs it has control over who can and cannot join their platform in addition to censoring content. A lot of social media platforms follow this centralized system. The decision-making lies with only a few people as followed by banks. When you want to transfer money to someone, you need to be authorized for the same by the bank.
Decentralization was a broad concept until the introduction of Bitcoin. When people exchange bitcoins, it doesn’t have to go through a centralized authority. The advantage here is that users are in complete control of their transactions. There is complete transparency of the records and these records can be verified by anyone. Another advantage is that the data here is immutable and cannot be changed.
Types of Blockchain
Now that we know what Blockchain means, let’s get into the different types of Blockchain. There are four types of Blockchain:
1. Public Blockchain
These are open and decentralized computer networks that can be accessed by anyone that wants to check the accuracy of a transaction. Bitcoin and Ethereum are examples of public Blockchain.
2. Private Blockchain
Private Blockchains are not open, and access to them is restricted. Those who wish to participate must first obtain authorization from the administrator of the system. Since one person controls who accesses it, it is centralized.
3. Hybrid Blockchain
Hybrid blockchains are a combination of public and private blockchains and contain centralized and decentralized features. A hybrid Blockchain is also called a Consortium.
4. Sidechain
A Sidechain is a Blockchain that runs parallel to the main Blockchain. It mainly allows users to move data and information between two chains and is much more efficient.
How does it work?
When we use traditional ledgers to store records, it also makes it easy to alter data, since you can easily edit, delete, or add records. As a result, you may have difficulty trusting the information.
Public blockchains solve this problem. In a public Blockchain, the transactions are stored in blocks and are vouched for by consensus mechanisms that also make sure new blocks are added to it, thus making it unalterable. Proof-ofwork is a type of consensus mechanism and it is also called Mining.
When you send bitcoins, you also have to pay a small fee to a network of computers to authenticate the validity of your transaction. Your transaction is then combined with other outstanding transactions in a queue to be included in a new block. The transactions are then validated by the computers and the Block is added to the network. The miner's fee is all the transaction charges in that particular block.
Every block in the network is given a unique key that also contains the previous blocks’ keys and information. As the process goes on, it makes it increasingly hard to edit or alter the data and this system is what makes a Blockchain secure.
In this fast-paced world, new and upcoming technologies seem daunting but are essential nonetheless. While this is still a fairly complex subject, I hope this blog achieved its objective by introducing a fundamental technology that is transforming the way we trust and transact.


